Call Lifecycle
Call Lifecycle
This page explains what happens during a call in SIPHON, end-to-end. The goal is to give you a stable mental model so the rest of the docs (Agents, Inbound Calling, Outbound Calling) feel predictable.
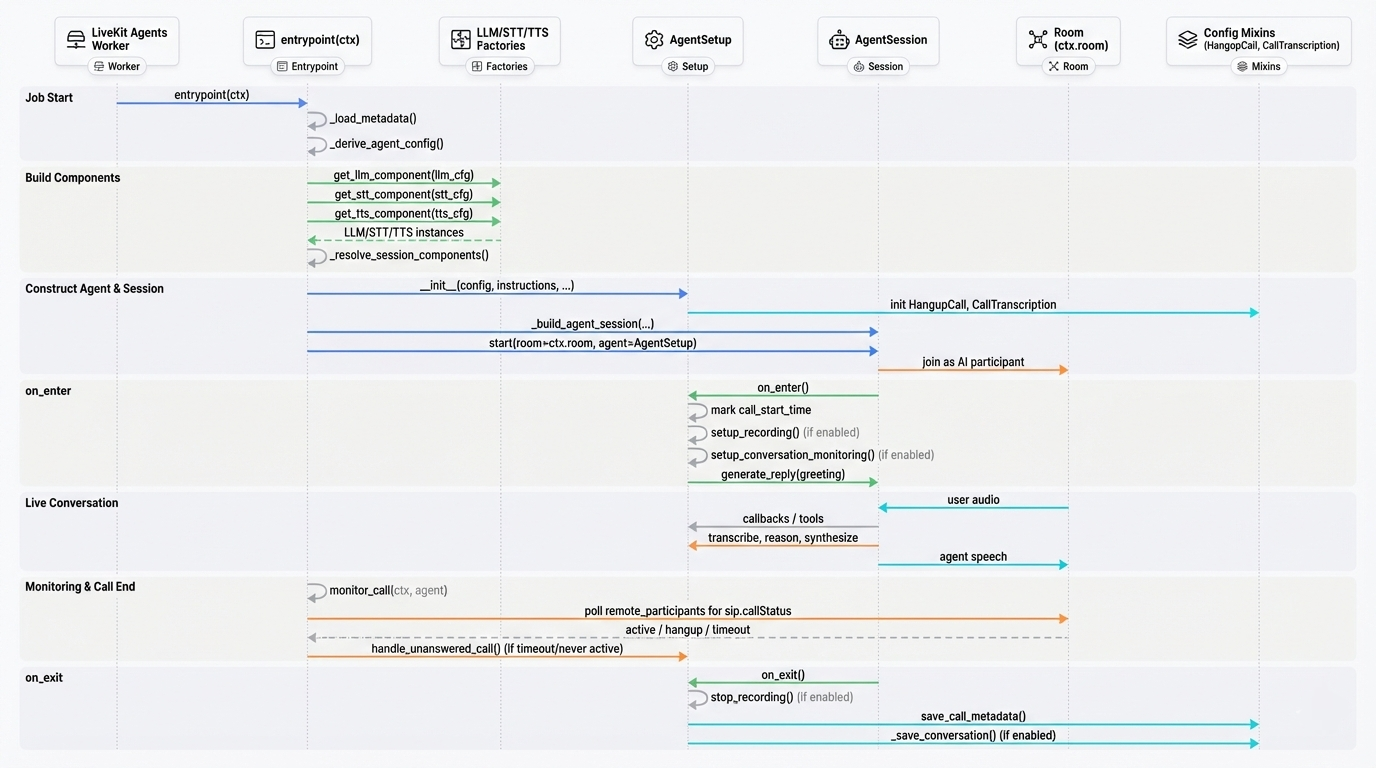
The building blocks
A SIPHON call always involves:
- An agent worker process you run (
Agent(...).dev()/Agent(...).start()) - SIP calling infrastructure (rooms, SIP participants, dispatch rules)
- Call configuration delivered as job metadata (including optional dynamic agent config)
Inbound call lifecycle (high level)
Inbound calls are “pulled” into your worker by a dispatch rule.
- A caller dials your inbound number.
- Your SIP provider forwards the call.
- SIPHON evaluates dispatch rules.
- A matching rule creates a room and assigns an agent name.
- Your agent worker receives the job and joins the room.
- The agent runs the conversation until the call ends.
Key idea: routing happens before the worker is involved. The worker only sees the job after a room exists and the dispatch has selected an agent_name.
Outbound call lifecycle (high level)
Outbound calls are “pushed” from your application code using Call.start().
- Your code creates a
Call(...)(numbers + trunk info + optional agent config). - SIPHON resolves an outbound trunk.
- SIPHON creates an agent dispatch for the target
agent_name. - SIPHON places the SIP call to the destination number.
- Your worker receives the job and joins the room.
- The agent runs the conversation until the call ends.
Key idea: for outbound, your code creates the call and the dispatch, instead of relying on a pre-existing inbound dispatch rule.
What the agent does during a call
Inside the worker, the agent lifecycle is conceptually:
- Join / initialize
- Apply base configuration from the worker.
- Apply optional per-call overrides from metadata (dynamic configuration).
- Speak / listen loop
- Transcribe audio (STT)
- Decide what to say (LLM)
- Generate speech (TTS)
- Optionally invoke tools
- Exit / cleanup
- Stop and persist call data if enabled (recording, metadata, transcription)
Failure modes (conceptual)
Common reasons a call fails:
- The worker is not running or
agent_namedoesn’t match - Trunk configuration is missing or invalid
- SIP provider rejects the call (auth, caller-id, number formatting)
- Required credentials are missing (
LIVEKIT_URL,LIVEKIT_API_KEY,LIVEKIT_API_SECRET)